|
|
 |
|
|
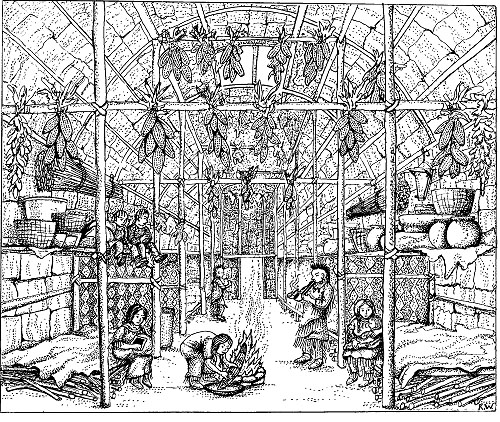
The bark of the longhouse was typically elm. There were plenty of elm trees available and the wood made good housing material because it offered protection from the rain and cold. In the winter, both ends of the longhouse were covered with animal fur to help keep the cold out and the heat in. |

|
| Longhouses
varied in length from about sixty to three hundred feet. They were divided
into sections. Each section served as a home for a family. Living within
the same house built a sense of community within the tribe and helped
make the best use of the natural resources. |
|
|
The
longhouse frame was built by forming a curved roof using flexible
poles or smaller trees. |
 |
This structure was created using tall timbers woven with saplings and large tree branches. |
